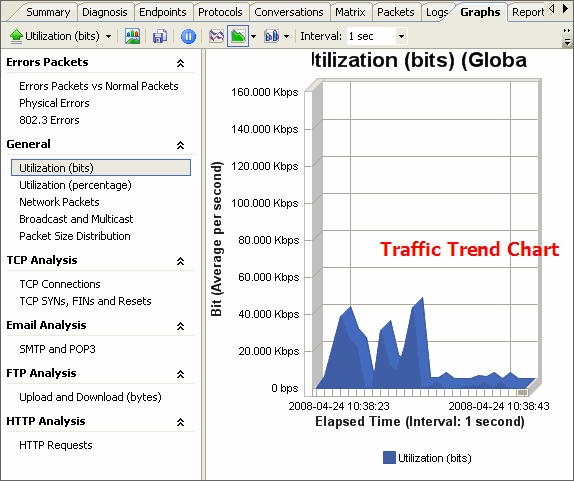
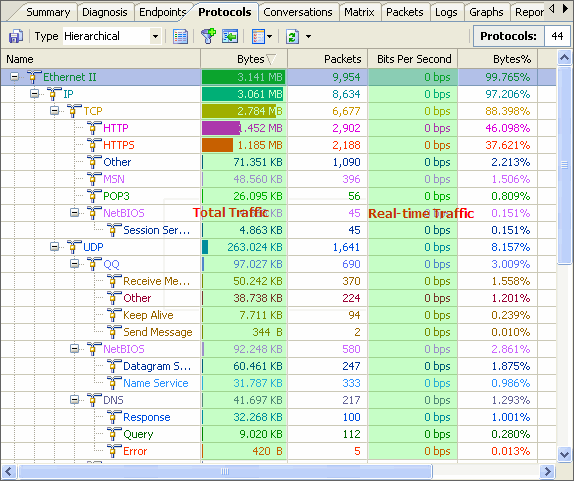
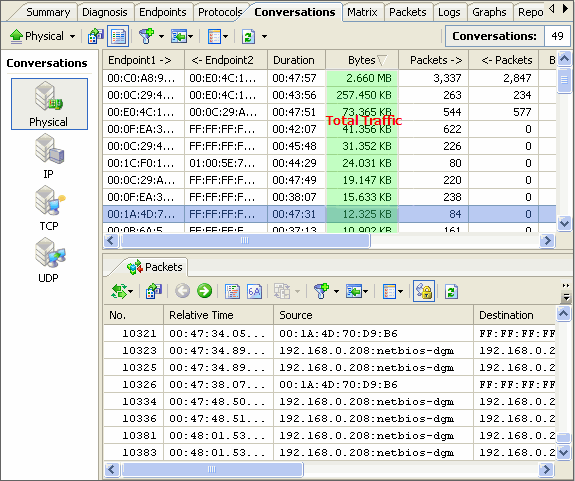
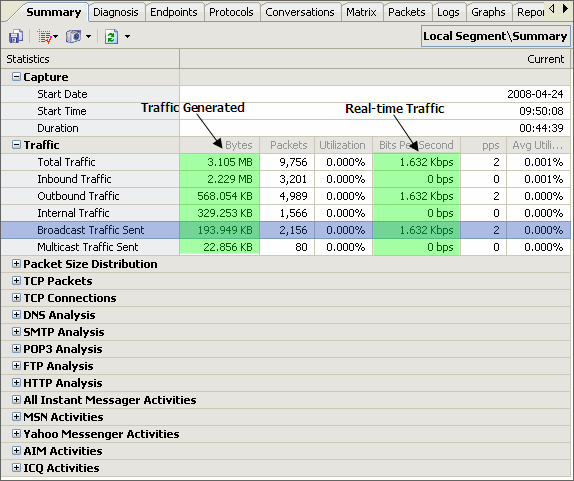
(colasoft.com) – Oct 21, 2008 - Colasoft, a dedicator in network analysis field, recently released version 6.9 of its flagship product – Capsa, a packet sniffer software designed for network monitoring and troubleshooting purpose. Two new protocols, Cisco Inter-Switch Link (ISL) and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) now can be recognized and decoded. This latest version also improved user’s experience based on user’s feedbacks.
(colasoft.com) – Oct 21, 2008 - Colasoft, a dedicator in network analysis field, recently released version 6.9 of its flagship product – Capsa, a packet sniffer software designed for network monitoring and troubleshooting purpose. Two new protocols, Cisco Inter-Switch Link (ISL) and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) now can be recognized and decoded. This latest version also improved user’s experience based on user’s feedbacks.Capsa is packet sniffer software which can perform real-time packet capturing, 24/7 network monitoring, advanced protocol analyzing, in-depth packet decoding, and automatic expert diagnosing. By giving users insights into all of the network's operations, Capsa makes it easy to isolate and solve network problems, identify network bottleneck and bandwidth use, and detect network vulnerabilities, external attacks and insecure applications.
"We'll always take into consideration good suggestions from our customers", Said Roy Luo, the CEO of Colasoft, "and include them in future releases to ensure highest satisfaction."
What’s New in Capsa 6.9
Support ISL Protocol Decoding: Cisco Inter-Switch Link (ISL) is a Cisco Systems proprietary protocol that maintains VLAN information as traffic flows between switches and routers, or switches and switches. It is a protocol to encapsulate traffic from different vlans, and tag them for latter specification. Now all trunk traffic between switch -- switch or router -- switch can be decoded and the context inside of the trunk link can be analyzed.
Support FCoE Protocol Decoding: Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a proposed mapping of Fibre Channel frames over selected full duplex IEEE 802.3 networks. This allows Fibre Channel to leverage 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification is supported by a large number of network and storage vendors, including Cisco, EMC, HP, IBM, Intel, and Sun Microsystems.
View IP address and Hostname in One Tab: Capsa will automatically resolve hostname and display it in its interface. In previous versions users may view only the hostname or the IP address at a time, they will need to switch manually if they want to view another value. In 6.9 users can directly view both the IP address and the hostname at the same time, which provides correlation between the two values
"It's the easiest product to use. The support is excellent and the features added in subsequent releases are always well thought-out and beneficial to our company." Eric Gomez, CSO, InfoSight, Inc.
Whether for a network administrator who needs to identify, diagnose, and solve network problems quickly, an IT professional who wants to monitor user activities on the network, a security manager who needs to ensure that the corporation's communications assets are safe, or a consultant who has to quickly solve network problems for clients, Capsa has the functions that satisfy the diversified needs perfectly.
Capsa 6.9 runs under Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista. A trial version is available at the company's web site: http://www.colasoft.com/
About Colasoft
Ever since 2001, Colasoft has been dedicated in providing all-in-one and easy-to-use network analysis software for customers to monitor, analyze, and troubleshoot their network. Up to now, more than 4000 customers in over 70 countries trust the flagship product – Capsa as their network monitoring and troubleshooting solution. The company also offers four free network utilities: Colasoft Packet Builder, Colasoft Packet Player, Colasoft MAC Scanner, and Colasoft Ping Tool. Learn more today at http://www.colasoft.com/